ALCOHOLIC DRINKS

Alcohol is regarded as the oldest and most widely used recreational drug. The production of wines, beer and distilled spirits is estimated to be a $300 billion-a-year worldwide business. In most Western countries about 80 percent of the population has said they have tried it and 50 percent say they are regular users. Pre-historic people drank beer and wine before they invented agriculture. Many Muslims drink it even though their religion forbids it.
The word "alcohol is derived form an Arabic word “al-kuhl” , which means "a powder for painting the eyelids." Alcoholic drinks are made from ethyl alcohol, also known as ethanol or grain alcohol. It is produced by the fermentation of sugar or starch. Methyl, also known as methanol or wood alcohol, is made distillation of wood. It and most other kinds of alcohol are poisonous and can be lethal. Methanol is often found in moonshine and is notorious for making people blind and killing them.
Without distillation, the highest alcohol content is 5 percent for beer and 11 to 12 percent for wine. Above these levels yeast no longer produce fermentation. Distillation can be used to produce 100 percent pure grain alcohol as well as whiskeys, vodka, rum, gin and other distilled spirits that generally have an alcohol content of around 40 percent. Proof numbers are double the percent numbers. A spirit that is 40 percent alcohol is 80 proof.
Websites and Resources: Drink Focus drinkfocus.com ; Alcoholic Drink.net alcoholicdrinks.net ; Wikipedia article Wikipedia ;International Center for Alcohol Policies Tables icap.org/table ; International Center for Alcohol Policies icap.org ; History of Alcoholic Beverages potsdam.edu/hansondj ; History of Alcohol nicks.com.au ; Alcohol in Ancient Egypt thekeep.org/~kunoichi/kunoichi/themestream/egypt_alcohol ;
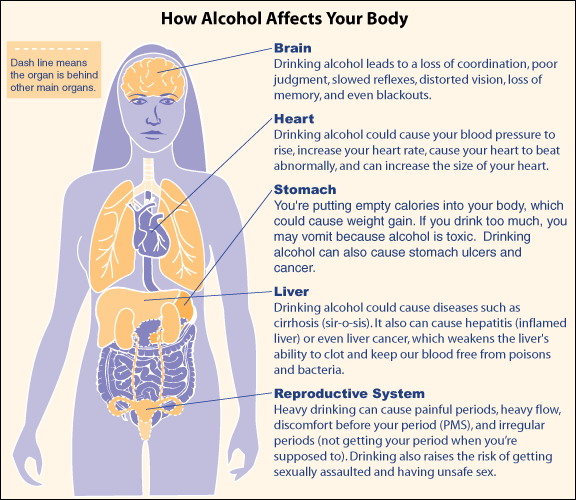
Alcohol, the Brain and Body
Alcohol creates an initial period of excitement, talkativeness and pleasure that last for a half hour or so, followed by a period sedation. Many people keep drinking to keep the initial buzz going and to intensify it.
Alcohol has certain physiological effects on the body, particularly the central nervous system. Ethanol is a relatively small molecule. After it is swallowed it is absorbed into the blood via small blood vessels in the stomach and intestines. On an empty stomach about 20 percent of the alcohol is absorbed by the stomach and 80 percent by the intestines and the alcohol reaches its peak in about an hour. Alcohol consumed with a meal is absorbed much more slowly and reaches its peak in two hours.
Once in the bloodstream alcohol heads for the nucleus accumbens, an area of the brain associated with pleasure, gratification, hunger, thirst, stress reduction and sex. It releases and increases the production of dopamine and other pleasure-inducing chemicals such as serotine (a neurotransmitter which produces a sense of well-being), and the brain's natural opiods. It also disturbs levels of glutamate, which cause neurons to fire and produces the initial alcohol high, and GABA, which reduces neuron firing and is what makes many drinkers sleepy.
Alcohol and Health

William Hogarth image Excessive drinking can lead to damage of the liver, brain and kidneys. It also is linked with increased risk of cancer and heart disease and cuts new pathways to the areas of the brain that over the long term negatively affect attention, memory and judgment. Alcoholics become psychologically and physically addicted. They build up stronger and stronger tolerances and need more and more alcohol to get a buzz. When they try quite they can experience nasty withdrawal symptoms, complete with tremors, hallucinations and sickness.
Death from alcohol is rare but it occurs, mainly when people drink a lot of alcohol in a very short time. Some people drink so much they get alcohol poisoning. Like someone suffering a heroin overdose, they slip unto unconsciousness, are impossible to rouse and after while their breathing slows until it stops. Others chock on vomit that block their airway. Others still get drunk and pass out in the cold or in the water and die of hypothermia or drown.
Women not only get drunk easier than men. They also are more likely suffer health problem from drinking smaller amounts of alcohol. Alcohol is passed easily from pregnant women to their fetuses. Children born to heavy drinking mothers are more likely to have health problems than those of non-drinkers.
A big deal has been made about the health benefits of drinking red wine. Studies have shown that drinking any kind of alcohol in moderation on a daily basis has the same health benefits of red wine and the overall benefits of drinking red wine are overstated anyway, and are comparable to benefits of eating nuts in moderation on a daily basis A study released in 2004 conformed the long-held belief that beer and to a lesser extent liquor but not wine consumption are linked with gout, a form of arthritis. The finding, based on surveys by a team at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston with 47,000 men over ten years, suggests that drinking two cans of beer a day increases the chance of getting gout by 2.4 times and two drinks of liquor increased the chance by 1.6 times and suggests that a non-alcoholic component of beer and liquor plays a role in causing gout attacks.
Alcohol Abuse and Addiction
Alcohol was listed as the fifth most harmful drug in a study by a team led by Prof. David Nutt of Britain’s Bristol University published in the British medical journal Lancet after heroin, cocaine, barbiturates and street methadone. Tobacco came in ninth. Cannabis came in 11th.
Antabuse is a drug that makes you throw up when you drink alcohol. One of the problems with it as a remedy for alcoholism is that an alcoholic who wants to drink can simply avoid taking it.
Heroin, cocaine, amphetamines, alcohol and nicotine are regarded as the five drugs hardest to give up. As of the late 2000s, 22 million Americans were hooked on at least one of these substances.
Drug-taking usually begins with a person taking the drug to get high. When addiction sets in the drug is taken just to feel normal. When addiction really takes hold consumption of the drug becomes instinctive, more important than food and more urgent and destructive and people need to take it to avoid pain and withdrawal.
Only about one in ten people that try an addictive drug actually become hooked on it. Geneticists have found gene variants that predispose people to addictions and that people vary in their innate sensitivity to dopamine. This partly explains why addiction seems to run in families. A gene that codes for a dopamine receptor designated D1 comes in several different types and concentrations of receptors. People with fewer receptors may receive less natural stimulation from dopamine and may feel a need to seek artificial highs from drugs.
For more detailed information see Heroin, Cocaine and Amphetamines
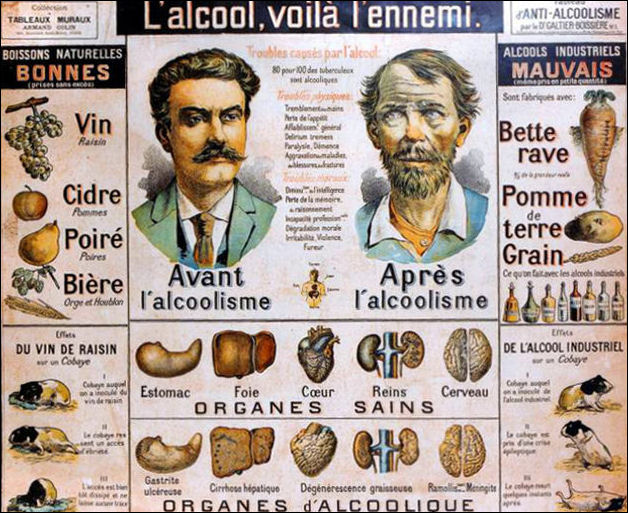
19th century French alcoholism poster
Addiction Treatments
Researchers are increasingly looking upon addiction as a disease that can be cured with medicine. Seeking treatments that fiddle with the dopamine system are dangerous in that dopamine is also vital to voluntary movement and messing with that can can cause symptoms resembling Parkinson’s disease.
Vigabatrin is a drug that stimulates the production of Gamma-aminobutyric acid, or GABA, a neurotransmitter that has an inhibitory effect on neurons. In one study, 30 percent of the cocaine addicts that took it were able to stay off the drug, compared to just 5 percent in a control group. What was perhaps most remarkable about the treatment was that it was effective with people written off as hopeless addicts.
Camparal is drug that has been on the market for a while as a treatment for alcoholism. It suppresses the brain chemical glutamate which is linked to cravings for drugs. Researchers are trying to develop a vaccine that would prevent drug users from getting high. An experimental cocaine vaccine is made of cocaine molecules attached to cholera-causing bacteria, which causes the immune system to respond by creating cocaine antibodies. If cocaine enters the body antibodies will bond to it preventing it from passing to the brain and triggering a buzz. Such a vaccine is already being studied under its first wave of large-scale clinical human trials. The same strategy is being used to develop vaccines for nicotine, heroin and methamphetamines.
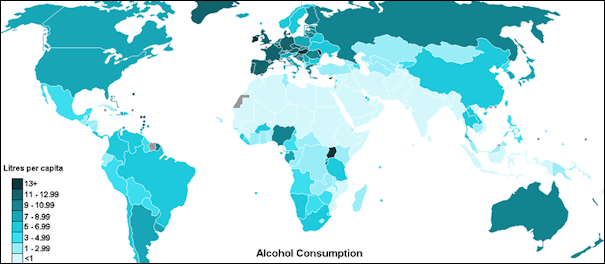
Alcohol consumption per capita world map
Image Sources: Wikimedia Commons
Text Sources: National Geographic, New York Times, Washington Post, Los Angeles Times, Smithsonian magazine, Natural History magazine, Discover magazine, Times of London, The New Yorker, Time, Newsweek, Reuters, AP, AFP, Lonely Planet Guides, Compton’s Encyclopedia and various books and other publications.
Last updated March 2011

