AGRICULTURE IN CHINA
 China feeds 22 percent of the world population with only seven percent of the planet's arable land. Land is heavily utilized for agriculture. Vegetables are planted on road embankments, in traffic triangles and right up the walls of many buildings. Even so since 1949 China has lost one fifth of its arable land. Only about 10 to 15 percent of the land in China is good for agriculture (compared to 1 percent in Saudi Arabia, 50 percent in India, 20 percent in the United States, and 32 percent in France). There is 545,960 square kilometers of irrigated land in China. Forty percent of China’s crop land is irrigated, compared to 23 percent in India. The average yield per acre in China is double that of India.
China feeds 22 percent of the world population with only seven percent of the planet's arable land. Land is heavily utilized for agriculture. Vegetables are planted on road embankments, in traffic triangles and right up the walls of many buildings. Even so since 1949 China has lost one fifth of its arable land. Only about 10 to 15 percent of the land in China is good for agriculture (compared to 1 percent in Saudi Arabia, 50 percent in India, 20 percent in the United States, and 32 percent in France). There is 545,960 square kilometers of irrigated land in China. Forty percent of China’s crop land is irrigated, compared to 23 percent in India. The average yield per acre in China is double that of India.
China traditionally has struggled to feed its large population. Even in the twentieth century, famines periodically ravaged China’s population. Great emphasis has always been put on agricultural production, but weather, wars, and politics often mitigated good intentions. With the onset of reforms in the late 1970s, the relative share of agriculture in the gross domestic product (GDP) began to increase annually. Driven by sharp rises in prices paid for crops and a trend toward privatization in agriculture, agricultural output increased from 30 percent of GDP in 1980 to 33 percent of GDP by 1983. Since then, however, agriculture has decreased its share in the economy at the same time that the services sector has increased. By 2004 agriculture (including forestry and fishing) produced only 15.2 percent of China’s GDP but still is huge by any measure. Some 46.9 percent of the total national workforce was engaged in agriculture, forestry, and fishing in 2004. [Source: Library of Congress]
China is the world’s top consumer of meat and grain. As it becomes more affluent people consume more meat and cooking oil and this has lead to increased demand for soybeans as an oil source and feed for livestock. China also uses more fertilizer that any other country.
David Pierson wrote in the Los Angeles Times, “In contrast to large, highly mechanized American farms, a typical Chinese farm is less than an acre in size and worked by hand. It's a legacy of communist reform, when the state seized control of China's farmland and subdivided it into tiny plots. Although this system has kept rural dwellers employed, it has slowed China's ability to boost their incomes.
With China’s accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001, food export opportunities have developed that have brought about still more efficient farming techniques. As a result, traditional areas such as grain production have decreased in favor of cash crops of vegetables and fruit for domestic and export trade. [Source: Library of Congress]
Improved farming policies and technologies have given China a high level of self-sufficiency and growth. But the country's top economic planning body warned that this would be hard to maintain. The lack of farm subsidies and expropriation of farmland for urban construction has crippled agriculture. As more farmers move to the cities, lured by better housing, education and other incentives, maintaining the food supply becomes more tenuous. One Chine agriculture expert told The Guardian, “We cannot be complacent. We know supply-and-demand is vulnerable. We have a forced balance now that requires strong intervention by the government. This is a tense balance that can be easily broken.”
Articles on AGRICULTURE IN CHINA factsanddetails.com and RURAL LIFE IN CHINA factsanddetails.com
Websites and Sources: Rice Culture of China china.org.cn ; Wikipedia article Wikipedia Products List and Links made-in-china.com ; China’s Ministry of Agriculture english.agri.gov.cn
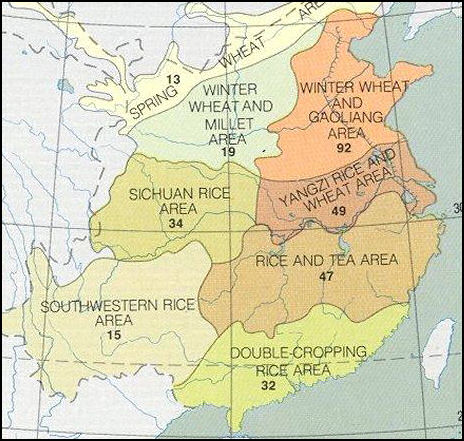
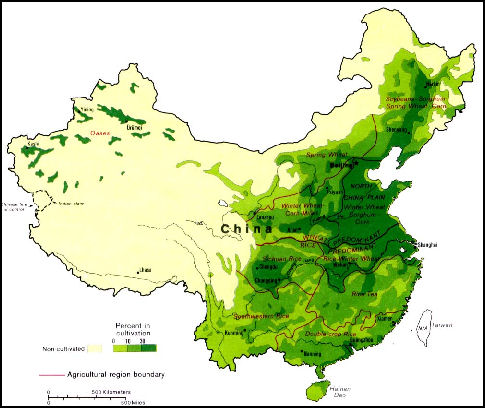
Agricultural Regions in China

Using all available land in Nanjing
Most of China is unproductive agriculturally. Arable land is concentrated in a band of river valleys and along the southern and eastern coasts.
Wheat, corn, soybeans, barley, kaoliang (sorghum), millet are grown in the north and central China. Rice is the dominate crop in the south. Some places produce double crops of rice. Most crops for export are grown in the coastal areas. These areas have relatively good roads and access to ports used for exporting produce.
The Northern Plain, which includes Beijing, is home to 65 percent of China’s agriculture but only 24 percent of it water. It produces half of China’s wheat and corn. It suffered from lower water table caused by too much pumping of water.
The Yangtze River delta is another important agricultural area. It is home to 30 million people and fertile soils produce a tenth of the country's crops. The crop yields there are expected to decline as large scale industries expand from nearby Shanghai and occupy productive agricultural land.
Mechanized agriculture makes more sense for northeast China which is made up largely of flat plain. Farms controlled by individual farmers and villages make more sense in the more mountainous southwest.
China is very mountainous. A lot of slopes and hillsides have terraces built on them so crops, particularly rice, can be grown on them. In barren Qinghai province, the only locally-grown food is raised in crude greenhouse made from plastic stretched over a bamboo frame.
See Global Warming
Agricultural Land in China
Farm land is still owned and controlled by the state and leased to farmers. It can not be bought or sold only leased. Land essentially belongs to local governments, a holdover from the commune era. Reforms passed in the Deng era allowed individuals to contract land from villages. To be converted into non-agricultural land it has to be reclaimed by the government and rezoned.
Peasants often have little say on the fate of the land they work even thought it may have been worked by their families for generations.
Most farmland is measured in mu, which is roughly equal to a sixth of an acre. On average a household tends a plot of land measuring 1.2 acres but can be as small as an eighth of an acre.
These days farmers sign 30-year leases for the right to work a plot and but they no longer are required to pay harvest quotas or most agricultural taxes. They don’t own the land, they can’t sell it and they can’t use it for collateral on a loan.
A policy approved by the Communist Party in October 2008 that aims to end rural poverty gives farmers the right to trade, rent, sublet, subcontract, engage in joint stock ownership and transfer their land rights. If all goes according to plan the move will help impoverished farmers double their income to $1,200 by 2020 and provide them with money they didn’t have before and create a huge new reserve of private wealth that will stimulate domestic spending and growth.
In 2011 The Economist reported: "Most of the land in China that can be farmed profitably is already under cultivation and that available land is actually shrinking in the face of development. In addition, yields are beginning to plateau with little expectation of major gains. After Mao Zedong died and land was opened up for commercial development, each plot came with only a 50-year government lease. No one knows what will happen when those leases expire. Yet building projects continue apace."
See separate article: Problems faced by Farmers in China
Chinese Farmers
Farmland in Sichuan
About 35 percent of China's labor force is in agriculture (compared to 2.5 percent in the U.S.). There are 425 million agricultural workers (200 million farming households) in China. A little over a decade ago China was home to 700 million farmers. They made up about 60 percent of the population.
A typical farmer earns 5,000 yuan a year from selling rice, wheat, canola, and pigs and has four acres he leases from the state. Taxes and fees eat about 4,000 yuan. School fees for children eat up another 2,000 yuan. Housing costs are minimal unless the farmer wants to make improvements or buy possessions. Most of their food they grow themselves.
Many farmers take outside jobs or buy a truck or receive remittances from a child or relative to make ends meet. They can usually cover expenses unless there is a string of weddings or funerals in which they have to fork out substantial gift payments.
Farmers typically live is a small brick house with electricity and a television. They have no pension and want their kids to go to university but don’t know how they will pay for it. Young people don't want to be farmers. One 21-year-old woman who left her village for a factory job told Reuters, “Nobody our age farms anymore. Nobody my age can plant a stalk. You need to leave to make real money.”
Farmer have suffered in modern China. Onw small factory owner told National Geographic, "Farmers find it hard to survive in an industrialized society. Farmer want to work in the factories, but transition is difficult and few of them adjust. They have no skills. They lack education. They lack the attitude one needs to learn. They have no sense of time, of living by the clock." The small-scale farmer is largely seen as a dying breed in China, made up mostly of the elderly left behind in the mass exodus of migrant workers to much higher-paying jobs in industrial cities.
See Rural Life, Problems Faced by Farmers
Increasingly Large Harvests in China
The autumn harvest typically accounts for three quarters of total grain production. China has had strong grain harvests from 2005 to 2010. Grain harvests in 2009 were a record 530.82 million tons.China The harvest was about 510 million tons in 2007. Grain production dropped from 512 million tons in 1998 to 430 million tons in 2003 and increased to 470 million tons in 2004 and 484 million tons in 2005 thanks to favorable weather and incentive to farmers. In 1993 China produced 440 million tons of wheat, rice and other grains.
According to United Nations statistics, China’s cereal production is the largest in the world. In 2003 China produced 377 million tons, or 18.1 percent of total world production. Its plant oil crops — at 15 million tons in 2003 — are a close second to those of the United States and amounted to 12.6 percent of total world production. More specifically, China’s principal crops in 2004 were rice (176 million tons), corn (132 million tons), sweet potatoes (105 million tons), wheat (91 million tons), sugarcane (89 million tons), and potatoes (70 million tons). Other grains, such as barley, buckwheat, millet, oats, rye, sorghum, and tritcale (a wheat-rye hybrid), added substantially to overall grain production. [Source: Library of Congress]
Crops of peanuts, rapeseed, soybeans, and sugar beets also were significant, as was vegetable production in 2004. Among the highest levels of production were cabbages, tomatoes, cucumbers, and dry onions. In 2004 fruit production also became a significant aspect of the agricultural market. China produced large crops of watermelons, cantaloupes, and other melons that year. Other significant orchard products were apples, citrus fruits, bananas, and mangoes. China, a nation of numerous cigarette smokers, also produced 2.4 million tons of tobacco leaves. [Source: Library of Congress]
Fertilizer use was a major contributor to these abundant harvests. In 2002 China consumed 25.4 million tons of nitrogenous fertilizers, or 30 percent of total world consumption and more than double the consumption of other major users such as India and the United States in the same period. Among the less used fertilizers, China also was a leader. It consumed 9.9 million tons of phosphate fertilizers (29.5 percent of the world total) and 4.2 million tons of potash fertilizers (18.2 percent of the world total).
Food Self-Sufficiency in China
Lauren Keane wrote in the Washington Post, “China has a long-standing policy of food self-sufficiency, growing 95 percent of the grain required to feed its people. The country's sheer size means that a major crop failure or other food emergency here could have international ramifications, overwhelming world food markets with sudden demand. "Were China to need to import a large amount of grain, it would have a very dramatic impact on world food prices," said Anthea Webb, director of World Food Program China. [Source:Lauren Keane, Washington Post, May 31, 2010]
The challenge of feeding a growing nation on a shrinking supply of arable land while confronting severe water shortages has long been a major concern here. China has to feed one-fifth of the world's population on one-tenth of its arable land, and the nation's expanding cities are consuming farmland at breakneck speed. China estimates that by 2030, when its population is expected to level off at roughly 1.5 billion, it will need to produce an additional 100 million tons of food each year.
Tan Ee Lyn of Reuters wrote: China’s agriculture minister said that China faced a formidable task in meeting demand for grains such as rice, wheat and corn over the next 10 years. Its water resources are meagre -- amounting to 25 percent of the per capita world average. And a quarter of its water is so polluted it is unfit even for industrial use. China's grain harvest stood at 530 million tonnes of grain in 2009 and it will need to increase annual supply by 4 million tonnes over the next 10 years. Beijing imported U.S. corn for the first time since 2006 and is the world's top buyer of soybeans. "In China, rice is the most important crop and it uses 50 percent of the freshwater China has each year," Chinese geneticist Zhang Gengyun told Reuters. [Source: Tan Ee Lyn, Reuters, September 17, 2010]
Howard Schneider wrote in the Washington Post, “China has remained largely self-sufficient in wheat, rice and corn. The government has encouraged production of these crops through measures such as setting base-line prices for farmers. To see how much longer China can remain self-sufficient, the markets for these staples are being watched closely by commodity trading companies, U.S. farmers, the World Bank and other organizations concerned with global food security. [Source: Howard Schneider, Washington Post May 22, 2011]
Grain and Food Imports in China
In 2012, the World Trade Organization (WTO) said that China had surpassed the United States to become the world’s largest importer of agricultural products. Even with 700 million farmers China is unable to meet the country;s demand grains, soy beans and other commodities.
China is increasingly importing corn to keep up with demand resulting in part from dietary changes and its use in producing biofuels. China relies on American farmers in particular for soybeans to use in animal feed. Last year, total U.S. soy exports were nearly $20 billion — triple the level of a decade ago.
In April 2012, the Financial Times reported: “China's grain imports hit a record high in March 2012, as the world's most populous country increasingly turns to overseas markets to meet its agricultural needs. Customs data from Beijing revealed that grain imports reached 1.64 million tonnes in March, up sixfold from a year earlier and up 50 percent from the previous month. China has to feed a fifth of the world's population with only 8 percent of the world's arable land, and does not grow genetically modified grains. As rising incomes and more meat-heavy diets boost grain demand, China's reliance on imports has slowly increased. [Source: Financial Times, April 10, 2012]
Big corn purchases likely contributed to the jump in grain imports, said traders. The grain category includes corn, wheat, rice and barley. China accounts for about 20 percent of the world's corn consumption and only 4 percent of global corn trade, but its sudden increase in corn buying has greatly tightened the global market. China's corn imports in January and February 2012 totaled 1.26 million tonnes, four hundred times more than the same period last year. China's domestic corn prices are among the highest in the world, and during January and February commercial firms were taking advantage of the arbitrage between Chinese and US corn prices to import corn at a profit.
Grain recorded the single biggest year-on-year jump in percentage terms of any commodity with a 500 percent increase, according to the customs data released. Analyst Ma Wenfeng at Beijing Orient Agribusiness said he expects China's grain imports to grow. He forecasts corn imports will hit 7 million tonnes in 2012, and wheat between 1.5 million to 2 million tonnes. "The key thing is the price," said Mr Ma. "Right now China's corn prices are incredibly high. . . if [state owned commodity trading house] Cofco can make money then it will import."
Others pointed out that mold and mildew had damaged some stored corn last year, contributing to tight domestic corn market. "Production [of corn] has increased significantly in China, but safe and secure storage have not grown in conjunction," said Rabobank analyst Daron Hoffman. Wheat imports have also soared. China's wheat imports in January and February were 580,000 tonnes, more than three times higher than the same period last year.
Modern Agriculture Technology, Tainted Food and Pollution
Most crops in China are raised with pesticides, chemical fertilizers and sewage sludge. Fertilizer is subsidized and is cheaper than its real cost. Farmers overuse it and overuse causes environmental damage.
China has very advanced agricultural research centers and laboratories that do research and churn out reams of data on the latest fertilizers, pollution risks and genetically-engineered crops The problem is that the data and insights these researchers come up with rarely finds its way to farmers, who mostly rely on the pesticide and fertilizer salesmen to keep them informed. Even then necessity often keeps them from following directions. Villagers given instructions to use the pesticides only once every 15 days are likely to use pesticides more frequently than that if their crops are being swarmed by insects.
These practices are sometimes blamed on high levels of chemicals found in agricultural products and in streams and rivers that receive a lot of agricultural run-off. Shipments of plums, lemons, star fruit, kumquts, scallions and ginseng to the United States have been blocked by U.S. Food and Drug Administration because of problems with pesticides and toxic additives.
In the 1980s, farmers were encouraged to use chemical pesticides and fertilizers to boost production. By the 2000s it had become clear that not only was the policy causing pollution and it was fouling agricultural land and reducing productivity. The government is now trying to encourage farmers tp come with alternatives to chemicals.
See Food Safety
Exploding Watermelons and Yard-Long Beans in China
“Watermelons have been bursting by the score in eastern China after farmers gave them overdoses of growth chemicals during wet weather, creating what state media called fields of “land mines,”" Alexa Olesen of Associated Press wrote. “Prices over the past year prompted many farmers to jump into the watermelon market. All of those with exploding melons apparently were first-time users of the growth accelerator forchlorfenuron, though it has been widely available for some time, CCTV said. [Source: Alexa Olesen, Associated Press, May 17, 2011]
About 20 farmers around Danyang city in Jiangsu province were affected, losing up to 115 acres (45 hectares) of melon, China Central Television (CCTV) said in an investigative report. Wang Liangju, a professor with College of Horticulture at Nanjing Agricultural University who has been to Danyang since the problems began to occur, said that forchlorfenuron is safe and effective when used properly. He told The Associated Press that the drug had been used too late into the season, and that recent heavy rain also raised the risk of the fruit cracking open. But he said the variety of melon also played a role.
"If it had been used on very young fruit, it wouldn't be a problem," Wang said. "Another reason is that the melon they were planting is a thin-rind variety and these kind are actually nicknamed the 'exploding melon' because they tend to split." Chinese regulations don't forbid the drug, and it is allowed in the U.S. on kiwi fruit and grapes. But the report underscores how farmers in China are abusing both legal and illegal chemicals, with many farms misusing pesticides and fertilizers.
Farmer Liu Mingsuo ended up with eight acres (three hectares) of ruined fruit and told CCTV that seeing his crop splitting open was like a knife cutting his heart. "On May 7, I came out and counted 80 (burst watermelons) but by the afternoon it was 100," Liu said. "Two days later I didn't bother to count anymore." Intact watermelons were being sold at a wholesale market in nearby Shanghai, the report said, but even those ones showed telltale signs of forchlorfenuron use: fibrous, misshapen fruit with mostly white instead of black seeds.
In March 2010, Chinese authorities found that "yard-long" beans from the southern city of Sanya had been treated with the banned pesticide isocarbophos. The tainted beans turned up in several provinces, and the central city of Wuhan announced it destroyed 3.5 tons of the vegetable. The government also has voiced alarm over the widespread overuse of food additives like dyes and sweeteners that retailers hope will make food more attractive and boost sales.
Though Chinese media remain under strict government control, domestic coverage of food safety scandals has become more aggressive in recent months, an apparent sign that the government has realized it needs help policing the troubled food industry. The CCTV report on watermelons quoted Feng Shuangqing, a professor at the China Agricultural University, as saying the problem showed that China needs to clarify its farm chemical standards and supervision to protect consumer health.The broadcaster described the watermelons as "land mines" and said they were exploding by the acre (hectare) in the Danyang area. Many of farmers resorted to chopping up the fruit and feeding it to fish and pigs, the report said.
Efforts to Increase Agricultural Production
Among the more radical steps being taken to increase production are using new strains of genetically modified rice and buying and cultivating land in neighboring countries such as Russia, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan by agricultural entrepreneurs. A spokesman for a Beijing research institute said the government is not involved in the cross-border expansion of Chinese farming. “We don't believe that going to rent and farm in other countries is a reliable policy option,” he told The Guardian. [Source: Jonathan Watts, The Guardian, February 23, 2010]
The Chinese government does not want to move towards the mega-farms seen in many other countries because a plot of land is a form of social security for the 850 million registered rural residents.
Increased Investments in Chinese Agriculture
In March 2009, China announced it would increase spending on agricultural production by 20 percent amid warnings of harmful effects of climate change, food shortages and food crises. As a central part of his annual budget speech at the Great Hall of the People Prime Minister Wen Jiabao's said an extra 121 billion yuan ($20 billion bn) would be spent on boosting farm yields and raising rural incomes. [Source: Jonathan Watts, The Guardian, March 5, 2009]
The government's spending aimed to boost overall domestic consumption with a strong emphasis on intensive agriculture. The short-term aim is to ease the impact of the economic crisis on rural dwellers and reduce sources of social instability and increase grain prices as an incentive for farmers to produce more.
Lei Ming, an environmental economist at Peking University said the extra spending on agriculture was a precautionary step. “The impact of climate change on food production is uncertain. It may go up, but it is also possible that we will face massive food shortages. To avoid such a risk, we need to prepare ourselves. I think that's one of the reasons the government is increasing the agriculture budget.”
Environmental groups said that the extra investment in rural infrastructure was welcome, but that it could prove counter-productive if not spent on sustainable farming. “If it is used to subsidize more chemical fertilizers that would be bad, but it could benefit both farmers and the environment if it was used to support eco-friendly cultivation,” said Sze Pangcheung, Greenpeace campaign director. “But that would require a big paradigm shift.” Currently, the focus of most funding and research in China is on intensive agriculture and genetic engineering.
Problems in Feeding the World's Largest Nation
For China to feed itself is a major undertaking. It has to feed 21 percent of world's people with 7 percent of the world's arable land. This means that China's entire population of 1.3 billion people China (four times as many people as in the United States) must be fed on arable land that covers less territory than the state of Texas. Massive famines have been a recurrent themes in Chinese history.
There are worries that China may not be able to produce enough corn, wheat and rice to feed its people and become dependant on foreign food sources and a slave to world food prices. Contributing to this problem are the urbanization or arable land, the scarcity of water and the exodus of labor from rural area to the cities. "China is losing the capacity to feed itself," wrote Lester Brown of the Worldwatch Institute in the Washington Post. "When that happens the food supply of the whole world will be affected, casting the shadow of global scarcity on humanity for the first time."
China has had strong grain harvests from 2005 to 2010. Grain harvests in 2009 were a record 530.82 million tons.”After five years of bumper harvests, it will be very difficult to keep grain production growing steadily,” the National Development and Reform Commission said in its annual report in 2009 , pledging to keep overall output in the coming year at least steady at 500 million tonnes. It is estimated that China will need to increase annual harvests by four million tons a year just to keep abreast of population growth. Satisfying the appetite of a population growing at the rate of 12 million people per year is all the more difficult as the impacts of climate change are felt.
The Worldwatch Institute estimates that if grain consumption per person in China were to equal the U.S. rate China would consumer two thirds of the world’s grain harvest To feed its huge population, China has to import foodstuffs from abroad. China sometimes exports rice and imports wheat and relies on American crops for more than a third of its food supply. The levels of grain reserves are kept secret. When shortfalls occur it is not clear his much grain is imported or how its taken frm reserves.
Even if China doubles its grain output in 20 years it still will not be able to feed each Chinese as well as he or she eats today. "If China fails to double it food production and instead continues to waste agricultural and water resources," one Chinese analyst told the New York Times, "then China will have to import 400 million tons of grain from the world market and I am afraid in that case that all the grain output of the United States could not meet China's needs."
Changing Eating Chinese Eating Habits and Agriculture
Howard Schneider wrote in the Washington Post, “For China, changes in food consumption are happening fast. In a nation where the word for rice is synonymous with food, people are eating less rice and other grains, preferring pork, fish and... chicken. Pig herds are swelling, and demand for some dairy products has been climbing 20 percent a year. Chinese imports of soybeans, a key animal feed, are booming. [Source: Howard Schneider, Washington Post May 22, 2011]
In China, food prices rose about 7 percent in 2010, according to official statistics, prompting the government to release some of its emergency reserves and put restrictions on sales of key staples such as wheat to try to prevent hoarding or speculation.
The changing diet can be seen throughout Beijing — from the young people hunkered around tables at a KFC, which has helped build a taste for chicken filet sandwiches, to the profusion of yogurt stocked on grocery shelves.”Particularly over the last two years, [Beijing] has become a huge market,” said a sales representative for Yilli, one of two major local dairy companies.
Agricultural regions
Meat, China's Food Shortages and the Rest of the World
As consumption of meat and dairy products has increased an increasing amount of land, water and resources has gone to feeding animals that produce them. "Incomes are climbing at a record rate, which means the consumption of meat is increasing even faster than the population — placing ever greater demand all along the food chain," Brown wrote. "When China's economic reforms were launched in 1978, only 7 percent of the grain was being used for animal feed. By 1990, that share had risen to some 20 percent, most of it used to produce pork. Now, demand for beef and poultry is also climbing. More meat means more grain — two kilograms of additional grain for each kilogram of poultry, four for pork and seven for each kilogram of beef." [Source: Lester Brown, Washington Post]
Reuters reported: China's per person consumption of meat is 70 kg (155 pounds) a year, of which 54 percent is pork. That will soar with rising incomes reflecting more affluent areas like Hong Kong, where per capita meat consumption is 120 kg a year, according to Rabobank. "The government wants to secure food supply. The demand is for fresh meat," said Jean-yves Chow, senior industry analyst at Rabobank in Hong Kong. "It doesn't want to rely on meat imports." [Source: Tan Ee Lyn, Reuters, September 17, 2010]
"Allowing only for the projected population increases with no rise in consumption per person, China's demand for grain would increase from 335 million tons in 1990 to 479 million in 2030. In other words even if China's booming economy produced no gains in consumption of meat, eggs and beer, a 20 percent drop in grain production (to 263 tons) would leave a shortfall of 216 million tons — a level that exceed the world's entire 1993 grain exports of 200 million tons...The reality is that no country, or combination of countries, could fill more than a small fraction of the potential food deficit forming in China. [Source: Lester Brown, Washington Post]
Chinese demand for grain is expected to make price rise significantly, which will in turn make food prices higher for consumers all around the globe.
Organic Food and Farming in China
In recent years, the Chinese upper and middle class have begun to embrace organic farming as a source of safe food as China has seen an unending string of food scandals: melamine-injected milk, counterfeit baby formula, bacteria-infected vegetables, pollution-poisoned fish and even cooking oil recycled from sewage. Research by Japanese companies such as Asahi Beer indicates that many farmers lack the knowledge on how ro use agricultural chemicals. [Source: William Wan, Washington Post, November 1, 2010]
A survey by the Chinese government in 2010 found that about 5 percent of produce examined was polluted with harmful substances in excess of government-set maximum levels. As is true with many things in China, there are reasonably good laws on the books for food safety but following and enforcing these laws is another story.
Organic milk can cost three times as much as regular milk but in some areas people are willing to pay the price to ensure the milk is free of chemicals and safe. Many ordinary Chinese take routine measures such as soaking vegetables in water to remove chemicals and ensure they are safe. On preparing vegetables such as winter melon and a housewife in Qingdao told the Yomiuri Shimbun, “I soak them in water for at least 30 minutes and often use salt to make sure they’re safe.”
Although organic produce stores are cropping up in Shanghai and Beijing, prices are high. Desperate for clean food at affordable prices, some Chinese families have formed cooperatives to buy directly from farmers — their own version of special supply. [Source: Barbara Demick, Los Angeles Times, September 16, 2011]
"There is not enough supply of organic food, there aren't so many farmers who really know how to produce organically, and if you found a farm, it is too expensive for ordinary people," said Liu Yujing, a Beijing homemaker who founded a 100-family cooperative last year. The mother of a 4-year-old girl, Liu was motivated by the revelations of melamine-tainted milk. "I know you can buy some organic food in shops, but I don't trust that either. We've heard a lot of them are fake."
Among China's new echelon of super-rich, organic food has become a luxury fad in high-end supermarkets in recent years - a status symbol like the latest Gucci purse. Imagine, one Chinese yuppie told the Washington Post knowing exactly where your food came from and what went into it.
Organic Farming for Communist Party Elite
Organic farmers say they face pressure to sell their limited output to official channels. "The local government would like us to give more products to officials and work units, but we think it is important that individuals can enjoy our product," said Wang Zhanli, whose organic dairy in Yanqing, just beyond the most frequented tourist sections of the Great Wall, received certification in 2006. [Source: Barbara Demick, Los Angeles Times, September 16, 2011]
At his Green Yard dairy, the technology is imported from Holland. The cows graze on grass free of pesticides and are milked in a sterile barn by women in white caps who look more like laboratory aides than milkmaids. On their organic diet, the cows produce about half the volume of conventional dairy cows, meaning that the supply is never enough, especially since the 2008 scandal in which tainted milk left six Chinese babies dead and sickened 300,000 people. Managers at the dairy say about two-thirds of their product goes to officials, state-owned enterprises, embassies and international schools. A limited quantity is sold at diplomatic compunds and a few select health food stores at prices nearly triple that for regular milk. "We're not Switzerland. Our population is way too big for everybody to eat organic food," said Hou Xuejun, general manager of the Green Yard dairy.
Organic Farms for Communist Party Elite
Barbara Demick wrote in the Los Angeles Times, “At a glance, it is clear this is no run-of-the-mill farm: A 6-foot spiked fence hems the meticulously planted vegetables and security guards control a cantilevered gate that glides open only to select cars. "It is for officials only. They produce organic vegetables, peppers, onions, beans, cauliflowers, but they don't sell to the public," said Li Xiuqin, 68, a lifelong Shunyi village resident who lives directly across the street from the farm but has never been inside. "Ordinary people can't go in there." [Source: Barbara Demick, Los Angeles Times, September 16, 2011]
Until May, a sign inside the gate identified the property as the Beijing Customs Administration Vegetable Base and Country Club. The placard was removed after a Chinese reporter sneaked inside and published a story about the farm producing organic food so clean the cucumbers could be eaten directly from the vine.
Elsewhere in the world, this might be something to boast about. Not in China. Organic gardening here is a hush-hush affair in which the cleanest, safest products are largely channeled to the rich and politically connected. In the capital, special supply farms are located near the airport, home to wealthier expatriates and many international schools, and to the northwest, beyond the miasma of pollution emanating from the overcrowded, traffic-choked central city.
The customs department said it did not own the farm but had signed a 10-year lease to buy vegetables. "Because of this deal we were able to have a stable supply of vegetables for the past years and we can pay for these items at much lower costs even when the price of food is rising so much nowadays," customs spokeswoman Feng Lijing said.
In the western foothills, the exclusive Jushan farm first developed to supply Mao's private kitchen still operates under the auspices of the state-run Capital Agribusiness Group, providing food for national meetings. A state-owned company, the Beijing 2nd Commercial Bureau, says on its website that it "supplies national banquets and meetings, which have become the cradle of safe food in Beijing." The State Council, China's highest administrative body, has its own supplier of delicacies, down to salted duck eggs.
"We have supplied them for almost 20 years," said a spokesman at the offices of Weishanhu Lotus Foods, in Shandong province. "Our product cannot be bought in an ordinary supermarket as our volume of production is very little."
Much of the pork for the elite is procured through the 2nd Commercial Bureau, which has a subsidiary that slaughters 50,000 pigs a year at a farm in Sanhe, Hebei province, according to Caixin, a business magazine. The magazine said most of the pork went to the special supply and quoted a manager as saying, "Sometimes raising pigs is about politics too."
Young Chinese Farmers Take Up Organic Farming
William Wan wrote in the Washington Post, “On an island called Chongming, a two-hour drive east of Shanghai, a group of young urban professionals has begun to buck the trend. They are giving up high-paying salaries in the city and applying their business and Internet savvy to once-abandoned properties. They are trying to teach customers concepts such as eating local and sustainability. And they are spearheading a fledgling movement that has long existed in the Western world but is only beginning to emerge in modern China: green living. [Source: William Wan, Washington Post, November 1, 2010]
"What we are trying to create is like a dream for us," said Chen Shuaijun, a young banker who, with his wife, has rented eight acres on Chongming. "But it is simply bizarre to everyone else," he added, with a sigh. Chen was the first in his family to go to college. He majored in computer science, got married and began climbing the ladder in Shanghai's banking industry. Then, one day last year, his wife, Shen Hui, pitched him a wild idea. Unlike Chen, she had grown up in the city and was tired of the smoggy air, the unnaturally green and almost tasteless grocery store broccoli and the fast-paced, high-pressure life in a cubicle. To her and a growing number of Chinese of her generation, the countryside represented a simpler paradise. But the biggest draw for her was food safety.
Chen's neighbors ridiculed him to his face when the couple announced that they wanted to leave Shanghai and become organic farmers. Co-workers expressed shock. And Chen's parents, who had toiled on farms just so he could study and go to college, became enraged. "There were some angry phone calls," Chen admitted.
Not that it got any easier once he launched his farm. Chen and his wife till their rented land on the weekends. But most of the peasants he hired to tend it during the week had never even heard the term organic and derided the organic methods he developed after months of online research. His parents, who eventually agreed to work the farm, and the hired peasants have even come close to mutinying at times against Chen's strict rule against pesticides and fertilizers.
For Chen and wife Shen, finding that balance this first year on their farm has driven them to exhaustion at times. Shen, who began as the more idealistic of the two, has found herself physically unable to get up some weekends after hours of weeding. She admits that her original plan for them to one day quit their jobs and work full time in the country may not be the best idea. "It gets boring in the country, because there isn't that much to do," she said. But the joys have outweighed the pains, she adds. This summer, she harvested their first tomato of the season. And she described the pleasure of biting into the red fruit and realizing for the first time what a real, unadulterated tomato tasted like. "There's nothing like that," she said, "in the city."
A few miles from Chen's farm, Han Guojie, 38, another new farmer, confessed, "We'll be losing money this year - a lot, in fact." Han gave up a high-paying job as a water quality engineer last year to start his farm. And he expects to be in the red for a while longer because the soil needs to recover from years of heavy chemicals and pesticides.
A devout Buddhist who carries prayer beads wherever he goes, Han says the motivation for him and other new farmers transcends the material. "For years, humans have tried to conquer nature, but in doing so, they themselves became conquered. They lost their connection with the earth. They destroyed the land they were tilling," Han said. "In Buddhist belief, there are no pesticides, no bad insects, no good ones. There is only imbalance in the world. We must restore that balance."
Most young farmers on the island had similarly lofty motives. Jia Ruiming, a former schoolteacher, began his organic rice farm after seeing the poverty of China's rural farmers. Most are in their 60s or older and unable to compete in the state-regulated system that produces most of China's food. He hopes to teach the older farmers he's hired that organic rice can sell for many times more than regular rice and wants to show them how to market it in Shanghai.
Difficulty of Organic Farming
William Wan wrote in the Washington Post, “Not using either has meant catching insects at times by hand, endless weeding in the fields and hauling in smelly, dirty "natural" fertilizers from nearby livestock. The family has lost their entire crop of corn three times to insects; only a handful of cucumbers survived the most recent season. And because the organic produce has more flaws, scars and uneven shapes than ordinary grocery-store vegetables, it's been hard to sell the little they've produced.
Even when their methods are sound, the water and soil such farmers use often are not because of rampant pollution.This summer, the government reported 43 percent of state-monitored rivers are so polluted, they're unsuitable for human contact.
The industry the farmers are trying to nurture is also - like most markets in China - plagued with fakes. Regulation on organic goods remains weak. Competing agencies offer varying degrees of certification and some, farmers say, will certify even the most pesticide- or hormone-injected goods for the right price. As a result, many new farmers like Chen bypass the organic certification altogether and simply call their goods "natural."
There are also harsh economic realities. The idea of paying up to 10 times more for organic produce remains foreign, not to mention out of reach, for most in China. But the toughest part for many of China's newest farmers is dealing with the cultural backlash. Farming in China is loaded with historical baggage. For centuries, it was looked down on as the job of low-class peasants, and then, under Mao, it was abruptly elevated to the noblest of proletarian professions. Now, in the midst of China's unbridled industrialization and urbanization, farming is once again considered one of the worst possible jobs in the country.
Image Sources: 1, 2, 7, 8, 10) Columbia University; 3, 4, 6, 11, 12 ) Nolls China website http://www.paulnoll.com/China/index.html ; 5) Louis Perrochon ; 9) FAO; 13) Agroecology; 14, 15) Landsberger Posters http://www.iisg.nl/~landsberger/
Text Sources: New York Times, Washington Post, Los Angeles Times, Times of London, National Geographic, The New Yorker, Time, Newsweek, Reuters, AP, Lonely Planet Guides, Compton’s Encyclopedia and various books and other publications.
Last updated January 2013
